Turbines
A turbine is a device that converts fluid energy into mechanical energy by guiding the fluid through stationary passages or vanes and directing it to exert torque on rotor blades, causing rotation.
präzitechproduct
Classification of Turbines
Turbines are classified into four types based on the working fluid:
1. Water Turbines
2. Steam Turbines
3. Gas Turbines
4. Wind Turbines
Industrial and Commercial Applications of Turbines
1. Power Generation
Turbines drive generators, converting mechanical energy into electricity, supporting both conventional and renewable energy plants.
2. Aerospace and Aviation
Gas turbines power turboprop and turbofan engines, ensuring efficient and safe aircraft propulsion.
3. Oil and Gas Industry
Turbines power gas compressor stations, pumps, and generators, ensuring efficient operations in refineries and petrochemical plants.
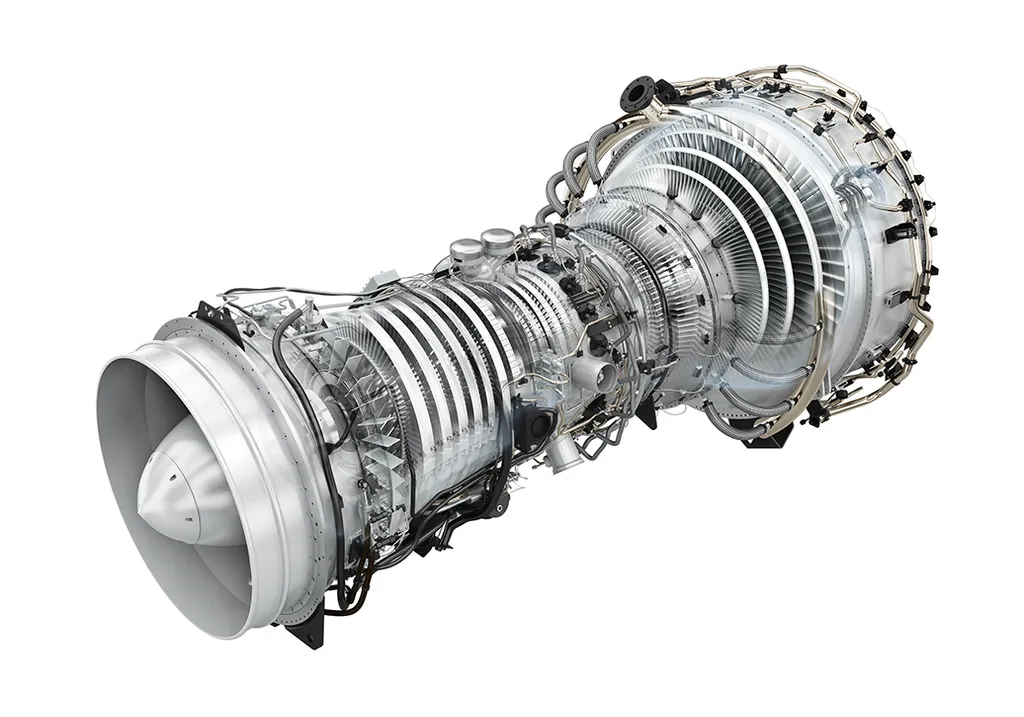
our Turbines types

Gas turbines are rotary engines that convert the energy of compressed and heated air mixed with fuel into mechanical energy, often used for power generation or propulsion. They operate in three main stages: compression, combustion, and expansion. Air is compressed, mixed with fuel, ignited in the combustion chamber, and then expelled through turbine blades, causing the rotor to spin. Gas turbines are valued for their high efficiency, quick start-up times, and versatility, finding applications in power plants, aircraft propulsion, and industrial processes. Their ability to use various fuels, including natural gas and liquid fuels, makes them a key component in modern energy systems.
( 0 products )

Gas turbines are rotary engines that convert the energy of compressed and heated air mixed with fuel into mechanical energy, often used for power generation or propulsion. They operate in three main stages: compression, combustion, and expansion. Air is compressed, mixed with fuel, ignited in the combustion chamber, and then expelled through turbine blades, causing the rotor to spin. Gas turbines are valued for their high efficiency, quick start-up times, and versatility, finding applications in power plants, aircraft propulsion, and industrial processes. Their ability to use various fuels, including natural gas and liquid fuels, makes them a key component in modern energy systems.
( 0 products )

Impulse turbines are a type of water turbine designed to convert the kinetic energy of high-velocity water jets into mechanical energy. They operate by directing water through nozzles at high speed onto curved blades or buckets, causing the turbine wheel to spin without the water fully surrounding it. Since impulse turbines rely solely on the velocity of water, they are ideal for high-head, low-flow conditions. Common examples include the **Pelton wheel** and **Turgo turbine**, which are widely used in hydroelectric power generation in mountainous regions with steep waterfalls or high-pressure streams.
( 0 products )

Impulse turbines are a type of water turbine designed to convert the kinetic energy of high-velocity water jets into mechanical energy. They operate by directing water through nozzles at high speed onto curved blades or buckets, causing the turbine wheel to spin without the water fully surrounding it. Since impulse turbines rely solely on the velocity of water, they are ideal for high-head, low-flow conditions. Common examples include the **Pelton wheel** and **Turgo turbine**, which are widely used in hydroelectric power generation in mountainous regions with steep waterfalls or high-pressure streams.
( 0 products )

Steam turbines are mechanical devices that convert thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical energy, typically used to generate electricity. They work by directing steam onto a series of blades mounted on a rotor, causing it to spin and drive a generator. Steam turbines are classified into **impulse** and **reaction** types, depending on how they extract energy from the steam. They are widely used in power plants, industrial processes, and marine propulsion systems, valued for their high efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle large power outputs.
( 0 products )

Steam turbines are mechanical devices that convert thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical energy, typically used to generate electricity. They work by directing steam onto a series of blades mounted on a rotor, causing it to spin and drive a generator. Steam turbines are classified into **impulse** and **reaction** types, depending on how they extract energy from the steam. They are widely used in power plants, industrial processes, and marine propulsion systems, valued for their high efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle large power outputs.
( 0 products )

Water turbines are mechanical devices that convert the kinetic and potential energy of flowing or falling water into mechanical energy, which is typically used to generate electricity. They operate by directing water through blades or vanes, causing the turbine to spin and drive a connected generator. Common types include impulse turbines, like Pelton wheels, for high-head, low-flow conditions, and reaction turbines, like Francis or Kaplan turbines, for lower-head, high-flow situations. Water turbines are integral to hydroelectric power plants and play a critical role in sustainable energy production worldwide.
( 0 products )

Water turbines are mechanical devices that convert the kinetic and potential energy of flowing or falling water into mechanical energy, which is typically used to generate electricity. They operate by directing water through blades or vanes, causing the turbine to spin and drive a connected generator. Common types include impulse turbines, like Pelton wheels, for high-head, low-flow conditions, and reaction turbines, like Francis or Kaplan turbines, for lower-head, high-flow situations. Water turbines are integral to hydroelectric power plants and play a critical role in sustainable energy production worldwide.
( 0 products )

Wind turbines are devices that convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electricity through a generator. They consist of blades connected to a rotor, which spins when wind flows over them, creating lift and rotation. Wind turbines are categorized into **horizontal-axis** and **vertical-axis** types, with horizontal-axis turbines being the most common. Widely used in renewable energy production, wind turbines are a key component of sustainable energy systems, providing a clean, efficient, and eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
( 0 products )

Wind turbines are devices that convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electricity through a generator. They consist of blades connected to a rotor, which spins when wind flows over them, creating lift and rotation. Wind turbines are categorized into **horizontal-axis** and **vertical-axis** types, with horizontal-axis turbines being the most common. Widely used in renewable energy production, wind turbines are a key component of sustainable energy systems, providing a clean, efficient, and eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
( 0 products )
our Turbines brands
No data was found
new Turbines products
Wind turbines are devices that convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electricity through a generator. They consist of blades connected to a rotor, which spins when wind flows over them, creating lift and rotation. Wind turbines are categorized into **horizontal-axis** and **vertical-axis** types, with horizontal-axis turbines being the most common. Widely used in renewable energy production, wind turbines are a key component of sustainable energy systems, providing a clean, efficient, and eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
Gas turbines are rotary engines that convert the energy of compressed and heated air mixed with fuel into mechanical energy, often used for power generation or propulsion. They operate in three main stages: compression, combustion, and expansion. Air is compressed, mixed with fuel, ignited in the combustion chamber, and then expelled through turbine blades, causing the rotor to spin. Gas turbines are valued for their high efficiency, quick start-up times, and versatility, finding applications in power plants, aircraft propulsion, and industrial processes. Their ability to use various fuels, including natural gas and liquid fuels, makes them a key component in modern energy systems.
Steam turbines are mechanical devices that convert thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical energy, typically used to generate electricity. They work by directing steam onto a series of blades mounted on a rotor, causing it to spin and drive a generator. Steam turbines are classified into **impulse** and **reaction** types, depending on how they extract energy from the steam. They are widely used in power plants, industrial processes, and marine propulsion systems, valued for their high efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle large power outputs.
Impulse turbines are a type of water turbine designed to convert the kinetic energy of high-velocity water jets into mechanical energy. They operate by directing water through nozzles at high speed onto curved blades or buckets, causing the turbine wheel to spin without the water fully surrounding it. Since impulse turbines rely solely on the velocity of water, they are ideal for high-head, low-flow conditions. Common examples include the **Pelton wheel** and **Turgo turbine**, which are widely used in hydroelectric power generation in mountainous regions with steep waterfalls or high-pressure streams.
Water turbines are mechanical devices that convert the kinetic and potential energy of flowing or falling water into mechanical energy, which is typically used to generate electricity. They operate by directing water through blades or vanes, causing the turbine to spin and drive a connected generator. Common types include impulse turbines, like Pelton wheels, for high-head, low-flow conditions, and reaction turbines, like Francis or Kaplan turbines, for lower-head, high-flow situations. Water turbines are integral to hydroelectric power plants and play a critical role in sustainable energy production worldwide.
contact for quotations
visit us
visit uor office HQ
Hammfelddamm 4a, 41460 Neuss
call us
mon-fri from 8am to 5pm
+4915560002948
